Bitcoin mining is a critical process that ensures the security, integrity, and continued growth of the Bitcoin network. It involves solving complex mathematical problems through computing power, which verifies transactions and adds them to a public ledger known as the blockchain. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of what Bitcoin mining is, exploring its impact, technology, benefits, and challenges.
Understanding the Basics of Bitcoin Mining

Before diving deep into the complexities of what is Bitcoin mining, it’s essential to understand its fundamental concepts and how it fits into the broader picture of cryptocurrency.
The Concept of Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Bitcoin mining lies blockchain technology, which serves as a decentralized ledger for all cryptocurrency transactions.
Blockchain is composed of blocks connected in a chain, where each block contains transaction data, timestamps, and unique cryptographic hashes.
This structure ensures that once information is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without altering every subsequent block, making it highly secure against fraud.
- Decentralization: The most significant feature of blockchain is decentralization, meaning there is no single authority controlling the system. This helps reduce the risks associated with central points of failure.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to anyone on the network. Users can verify transactions independently, increasing trust in the system.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to change or erase. This features enhances security and reliability.
The Role of Miners in the Bitcoin Network
In the ecosystem of Bitcoin, miners play an indispensable role by validating and confirming transactions.
When users initiate a Bitcoin transaction, it gets bundled with other transactions into a block. Miners compete to solve a complex puzzle known as Proof-of-Work (PoW), which involves finding a specific hash that meets predetermined criteria.
The first miner to solve this puzzle gets the right to add the new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
- Security: Miners uphold the security of the network by ensuring that all transactions are valid and not double-spent.
- Consensus mechanism: The competition among miners creates a consensus mechanism that maintains the integrity of the blockchain.
- Incentives: Through mining rewards and transaction fees, miners are incentivized to continue supporting the network.
Mining Hardware: The Backbone of Bitcoin Mining
The hardware used in Bitcoin mining has evolved dramatically since the inception of Bitcoin, impacting mining efficiency and profitability.
Initially, miners used standard computers equipped with CPUs, but as more people joined the network, the difficulty of mining increased.
Today, specialized hardware known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) dominates the landscape due to their unparalleled processing power and energy efficiency.
- ASICs: These devices are designed specifically for mining Bitcoin, allowing miners to achieve significantly higher hash rates compared to traditional GPUs or CPUs.
- Energy Consumption: With the rise of ASICs, energy consumption has become a crucial factor in Bitcoin mining, driving discussions around ecological impacts and sustainability.
- Costs: The initial investment in mining hardware can be substantial, but it often pays off if managed effectively.
The Economic Implications of Bitcoin Mining
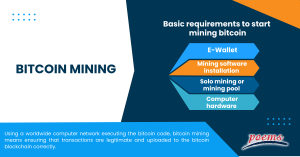
Understanding what is Bitcoin mining also necessitates exploring its economic implications, including its impact on the Bitcoin ecosystem, energy consumption, and regulatory considerations.
Mining Economics: Rewards and Costs
Mining Bitcoin comes with inherent costs and rewards that miners must balance to operate profitably.
The primary reward for successful mining includes:
- Block Rewards: Miners receive a set number of bitcoins for each block they successfully mine. As of 2023, the reward is halved approximately every four years through an event known as the “halving.”
- Transaction Fees: In addition to block rewards, miners earn fees from users who prioritize faster transaction confirmation.
However, the operational costs can be significant:
- Electricity Costs: Mining requires immense computational power, leading to high electricity bills, particularly in regions where energy is scarce.
- Hardware Depreciation: Mining equipment can become obsolete rapidly due to technological advancements, leading to significant capital losses.
- Maintenance: Upkeep of mining rigs and cooling systems can incur further expenses.
Market Dynamics and Price Influence
Bitcoin mining does not exist in a vacuum; it interacts dynamically with market trends and price fluctuations.
When Bitcoin prices soar, mining becomes more lucrative, drawing new entrants into the field. Conversely, when prices drop, many miners may find it unprofitable to continue operations, thereby reducing overall network security.
- Difficulty Adjustment: The Bitcoin protocol automatically adjusts mining difficulty approximately every two weeks to ensure that blocks are mined at a consistent rate.
- Market Sentiment: Public perception and sentiment toward Bitcoin can lead to rapid shifts in mining activity, impacting both security and profitability.
- Sustainability Concerns: As awareness of climate change grows, many stakeholders in the cryptocurrency space are advocating for greener mining solutions and renewable energy sources.
Regulatory Landscape and Its Impact on Miners
As Bitcoin continues to gain traction, governments worldwide are beginning to regulate mining activities, which can significantly affect miners’ operations.
- Licensing and Compliance: Some jurisdictions require miners to obtain licenses or adhere to specific standards, adding bureaucratic layers to operations.
- Taxation Policies: Many countries tax cryptocurrency mining profits, influencing miners’ bottom lines.
- Public Opinion and Policy: Growing environmental concerns could lead to stricter regulations aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of mining operations.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining: Trends and Innovations
As we consider what is Bitcoin mining, it’s crucial to examine the future possibilities and innovations shaping the industry.
Advancements in Mining Technology
Technological advancements continue to transform Bitcoin mining, enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
- Next-Generation ASICs: Manufacturers are constantly innovating to produce more energy-efficient and powerful ASICs, allowing miners to maximize their outputs while minimizing energy consumption.
- Cloud Mining Services: Cloud mining allows individuals to rent mining power without needing physical hardware. This model democratizes access to mining opportunities, albeit at the risk of profitability.
- Hybrid Mining Systems: Combining both Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake mechanisms may emerge as a trend, leveraging the strengths of both systems to enhance security and efficiency.
The Shift Towards Sustainable Mining Practices
With rising environmental concerns, the focus on sustainable practices in Bitcoin mining is becoming increasingly important.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Miners are exploring alternative energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Energy Efficiency Improvement: Companies are developing technologies that minimize energy waste during the mining process, promoting long-term viability.
- Carbon Offsetting: Initiatives aimed at offsetting carbon emissions associated with mining operations are gaining traction, attracting environmentally conscious investors.
Geopolitical Factors Affecting Mining Operations
Bitcoin mining is inherently tied to geopolitical dynamics, with different regions offering varying levels of support and resistance to mining activities.
- China’s Crackdown: China’s ban on cryptocurrency mining led to a massive shift in the global mining landscape, pushing miners to relocate to friendlier jurisdictions.
- Incentive Programs: Various countries are implementing incentive programs to attract miners, contributing to local economies and job creation.
- Geographical Concentration Risks: Concentrating mining activities in specific regions increases vulnerability to regulatory crackdowns, natural disasters, and socio-economic disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, what is Bitcoin mining goes beyond mere technicalities; it encompasses economic principles, technological innovations, and the evolving regulatory landscape. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem grows and matures, Bitcoin mining remains a vital component that fuels its ongoing development while facing challenges and opportunities for the future. By understanding these aspects, one can appreciate better the importance of mining in the world of digital currencies.